Graphics Card Ports Explained - HDMI, DVI, VGA, USB-C VirtualLink
Modern computers consist of graphics cards with a number of ports that connect to other devices such as monitors and TVs to display different video and audio streams. With the numerous ports available in the market, choosing one to use for your display can be very challenging. Understanding each type and its functionality can be of great help when it comes to the selection.
Table of Contents
Graphics Card Ports Compared
| Port | Resolutions | Analog Or Digital | Can Transfer | Used in |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VGA | 640 x 480 originally but has had updates so can do 1080p | Analog Only | Video Only | Old CRT and older displays |
| DVI | 2048 x 1536 @ 60 Hz (Dual Link), 1920 x 1080 @ 60 Hz (Single Link) | DVI-I is analog and digital, DVI-D is digital only, DVI-A is analog only | Video Only | Newer monitors but not the newest. Starting to go out of use. |
| HDMI | 3840 x 2160 @ 60 Hz using HDMI 2.0 | Digital Only | Video and Sound | TVs, games consoles, monitors and a lot of others. |
| Display Port | 5120 x 2800 @ 60 Hz with Display Port 1.4 | Digital Only | Video and Sound | Display Port 1.4a, HDMI 2.0b, DL-DVI-D |
| USB-C VirtualLink | Can do very high resolutions over 4K | Digital Only | Video, Sound and Power | VR Headsets mainly. But can be used like any USB-C Port. |
VGA

This type of graphics card port has been in use for the longest time, with both older machine models and newer ones having it. It has been in use since 1987 when IBM first introduced it. It has 15 pin connectors and, as such, is sometimes referred to as HD15 port. After its conception, the port became widely used, with many manufacturers still preferring to include it in PCs and laptops.
The VGA port is an analog connection that was mainly used to connect to CRT monitors. Its main function is to connect graphics cards to the monitors which receive the information in an analog form. Unlike digital display monitors that receive information in the pulsating form, analog ones receive continuous information. The wide use of CRT displays in many business premises is believed to be why these graphic ports are still being made.
The VGA port is only capable of delivering and receiving analog connections. A graphics card’s output is digital, which means that the signal has to be converted into an analog form before it is sent through the cable to the display monitor. Therefore, the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) plays a role in the quality of the images displayed at the monitor. It needs a high resolution to produce quality colors and picture.
VGA only transfers a video stream and has no sound unlike other newer ports. For this reason and the fact that it is analog, converting VGA to HDMI, DisplayPort or DVI usually involves a more complicated setup. Not just a simple VGA to HDMI cable. The VGA to HDMI adaptor usually has an analogue to digital converter and it also takes in sound from a 3.5mm jack to be able to convert the signal. That’s why VGA to HDMI adaptors have a small box – to house the ADC.
| Positives | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Lots of older displays use it | Analog Only |
| Still widely used | More difficult to convert to HDMI or DP |
| max res was 640 x 480 @60Hz but has evolved a lot. Can now support upwards of 1440p | Image quality can be lost as it depends on DAC |
| Cheap |
DVI

Digital Video Interfaces has been in use over the last 10 years, and that is part of the reason why VGA use has reduced considerably. These ports are mostly used with digital displays like LCDs, and they use Transition Minimized Differential Signaling. DVI connectors mostly operate at the highest signal of 1.65 gigabytes per second.
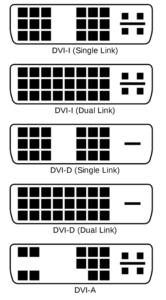
Dual Link DVI-D and DVI-I
Dual Link DVI-D and Dual-Link DVI-I: dual-link DVI-I links have 29 pins, whereas DVI-D dual links have 25 pins. Signals that are transmitted through DVI-D can be supported on HDMI and Display Port connectors. The DVI-D cable supports only digital output Whereas the DVI-I supports both digital and analog. Those that support such signals simultaneously have DVI-D and VGA connectors. Most monitors have DVI-D connectors.
The Dual Link part means that they have extra pins in the middle which allow for higher resolutions of about 2048 x 1536 @ 60Hz.
Single Link DVI-D and DVI-I
Single Link DVI-D and Single Link DVI-I: single-link DVI-I connectors are made with a total of 23 pins. They can’t convert digital and analog signals, but they do accept those signals in their form. Analogue and digital signals also can’t be transmitted through the cables at the same time. The user has to select one mode to use at a time.
Although DVI-I connectors work with different types of cables, the male connector of a dvi-i cable cannot fit into the female port of any other DVI due to their design. On the other hand, single-link DVI-D connectors have 19 pins, and they can work with DVI-I connectors.
The Single Link part means they don’t have extra pins in the middle and thus only support a lower resolution of 1920 x 1080 @ 60Hz.
DVI-A
The DVI-A is fairly uncommon and not widely used. It supports an anolog only signal and is not very useful in today’s digital world. However, it makes connecting old hardware a lot easier as the it runs on analog. It uses just 17 pins as it only needs the analog component.
| Positives | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Lots of options to choose from dvi | Can be complicated |
| DVI-I supports digital and analog | No sound |
| Good picture quality and resolutions can be achieved | Need the correct cable. DVI-D will fit in DVI-I but not the other way arround |
HDMI

High Definition Multimedia Interface is another graphics card port used in the transfer of digital data. The port is widely used in business and homes alike, with many people using it to connect to monitors, TVs, and other modern display monitors.
HDMI usually operates similar to that of DVI, with the only difference being that it can transfer up to 8 channels of data over the same channel. The signals being transferred can also be compressed or uncompressed. But either way, the quality of the video will be maintained.
Launched in 2002, HDMI ports have continued to increase in popularity and have also changed to become one of the best ports. One of the features that have improved with time is the ability to transmit high-resolution images. They have also been made compatible with 3D and have had ethernet channels included in them.
The improvement in HDMI features has made it the digital connection option of choice for most people. They still use HDCP encryption, and most brands choose to put them on their graphics card. HDMI has the advantage over DVI as it can transfer sound and video is one single cable. Furthermore it is capable of producing high resolution images of over 4k (if you use the right cable. HDMI 2.0 and above gives 4k @ 60Hz).
| Positives | Negatives |
|---|---|
| 4K @ 60Hz | Can be expensive |
| Can have ethernet and 3D | |
| Widely used | |
| Very simple and easy to setup as it transfers sound and video |
Display Port

Compared to other graphics card ports, Display Port is relatively new. This was introduced in 2007 with the main function of replacing VGA and DVI ports. With 20 pins, this port can be used in dual mode configuration. It also transmits data by using differential data pairs.
Display port can operate at different speeds with a four-pair connection over 17 gigabits of data per second. A display port comes with optional HDCP and content protection features as well.
Display port has already been widely adapted, with most people opting to use it instead. Computer chip brands have also opted to include Display Port into pretty much all machines they are producing. For instance, AMD was considering having multi-monitor features that increase usability. With the ability to connect up to 6 displays, these cards will be perfect for multiple uses simultaneously, which will make them great for gaming.
They did this and now lots of Display Port connectors are usually on a single graphics card so you have the option to have multi monitor setups of 6 or more displays.
Display Port, like HDMI, also supports video and audio to be transferred within one cable. However, Display Port is considered better as it supports much high resolutions and refresh rates. For instance Display Port 1.4 can support 5120 x 2800 @ 60Hz with a bandwidth of 25.92 Gbps.
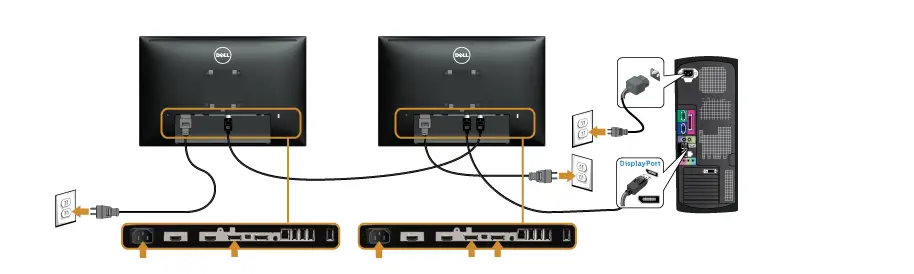
Display Port can also support multiple monitors through one port which no other port can do (not mirroring). It’s called daisy chaining and involves the first monitor being connected to the first port and then the other monitor being connected to the monitor that’s already plugged in.
| Positives | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Great resolutions and refresh rates | Can be more expensive |
| Low input lag | Not available on all displays |
| Transfers Sound and Video | |
| Daisy Chain monitors to use 1 port |
USB-C VirtualLink

As the needs of users continue to grow, the solutions in terms of connectivity also improve. VirtualLink allows the connection of VR headsets to you graphics card to allow the transfer of data and power. It is supported by some major companies including Nvidia, AMD, Oculus, Microsoft and Valve.
These connections are used for video graphics as well as audio, and they rely on USB-C connections. The main goal of this concept was to make it easier for users to transmit different video and audio directly to headsets over a single cable.
With USB-C VirtualLink, users can reduce the number of components they use to connect to different devices to transfer data. This is because it can transfer everything a VR headset needs including, power, audio and video.
Currently, VirtualLink technology is only viable in VR technology devices, but having type C USB being able to transfer video, data, and power on the same cable shows that soon VirtualLink will also have a better application.You can still use the USB-C port as a normal USB-C port as if it was on your PC. It will act in the exact same way as any USB-C.
| Positives | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Transfers Video, Audio and Power | Not yet utilized well |
| Useful for VR | |
| Thin Cable as it uses USB-C | |
| Good resolutions |
Which Port Should You Use?
There are many ports to choose from and some have better features than others.
If you’re using a monitor we recommend using DisplayPort unless your monitor doesn’t have DisplayPort. DisplayPort is one of the newer ports and supports large resolutions and high refresh rates with minimal input lag. This makes it perfect for monitors. If your monitor doesn’t have display port then we recommend using one of the ports in the following order: HDMI, DVI, VGA.
If you want to connect to a TV then your best bet is using HDMI. It provides both the sound and video with good resolution and refresh rates. TVs tend not to have DisplayPort ports so HDMI is useful to connect TVs.
Legacy monitors and displays should use whichever ports they have. This is most likely DVI or VGA.
For VR headsets you should use USB-C VirtualLink when possible but if your headset or graphics card doesn’t support these then use DisplayPort, or HDMI if it doesn’t support DP.
Conclusion
Out of all these graphics card ports, VGA is the oldest and is rarely used. It is still readily available for legacy reasons as older hardware is still used in many places. Having said this, newer hardware will be very unlikely to include any VGA ports. The graphics card’s port that is sometimes used even on newer hardware is the digital output version of DVI.
HDMI functions like DVI, but also transfers audio signals, making it perfect for electronic devices like TVs and game consoles.
Display Port is one of the newest ports, and it is an improvement over VGA, DVI and HDMI with a lot more potential. It has the ability for very high resolutions and refresh rates.
USB-C VirtualLink is very new, and it still has a lot of room for improvement. It could be a very good connection as it can transfer video, audio and power all at the same time. USB-C however is now no longer included on the latest Nvidia graphics cards and is now abandoned as it never made any progress in the VR headset market.