APU Vs CPU Vs GPU - Difference Between APU, CPU and GPU
In any gaming PC or console, graphics can make or break your experience. Gone are the days of video games with just large blocks of pixels and minimal details. Now, gaming experiences are grounded in realism.
People want a great story, unfolding in a somewhat realistic background with visually stimulating and relatable characters. Not talking or moving blocks of pixels.
Smooth frames, 3D rendering, special effects, the power to zoom and fast motion is what adventurists want now. So, which processors should you go for when building your gaming console? Because it all lies in the processors.
Should you opt for a CPU/APU with integrated graphics or go with a dedicated GPU and CPU. Graphics bring characters to life. Here is the difference between the three types of processors.
Table of Contents
Check more articles
Quick Compare Table - APU Vs CPU Vs GPU
| Term | Simple Explaination |
|---|---|
| CPU | A CPU is the central processing unit. It is the most essential component of a computer; without it, no instructions are executed. A CPU is a bunch of microelectronics called transistors that operate on electrical currents to implement basic logical operations, And, Or, Not as per a program's instructions. Need a CPU in any PC. |
| GPU | A GPU is also called a graphics card, also known as a video card. But a GPU refers to the graphics processing unit which is the processor on the graphics card's board. GPUs take information and turn it into frames. The speed of a GPU is measured in MHz and performance is measured by frame rate -how many frames it outputs per second. Good at processings graphics data to process high polygon and complicated 3d designs. Dedicated GPU is optional if your CPU has an Integrated GPU (IGPU). |
| APU | An Accelerated Processing Unit is a type of processor offered by AMD that can serve as a CPU and GPU at the same time. Most modern CPUs come integrated with GPUs, i.e., Integrated Graphics, but only the APU from AMD offers the combination of a GPU and CPU in a single die and HSA support. |
What is a CPU?

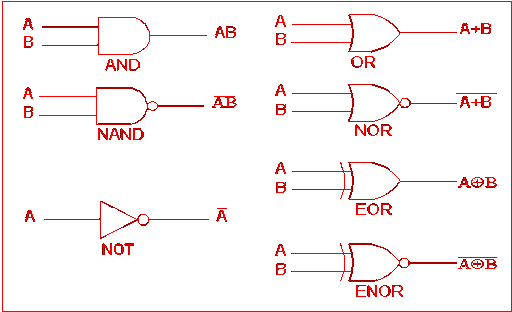
A CPU is the central processing unit. It is the most essential component of a computer; without it, no instructions are executed. A CPU is a bunch of microelectronics called transistors that operate on electrical currents to implement basic logical operations, And, Or, Not as per a program’s instructions.
Once the data is executed by the CPU, the output is sent to output interfaces. So in layman’s language, the CPU coordinates all activities of a computer.
Clock cycles per second
Most processors are synchronous; they use a clock to time when instructions occur. Synchronous CPUs always handle the same number of instructions per clock cycle. And the number of clock cycles per second is the speed of the processor.
In asynchronous processors, different things happen at different rates. These types of processors are only theoretical. In the past, to get more out of a processor, the trick has been to up the clock speed. For example, from 1 MHZ (one million cycles per second) to 3 -4 GHZ (a thousand million cycles per second).
RISC
RISC is a reduced instruction set computer; the opposite of a CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer).
Researchers at IBM discovered that processors supported hundreds of instructions while only using a few most of the time. So, to make processors faster, the core (tailored) instructions were optimized to work as quickly as possible.
RISC processors achieved speed by implementing minimal sets of instructions as efficiently as possible than CISC processors. But still, there is very little that can be done to make the RISC processor faster so it comes OoO.
OoO stands for Out of Order Execution. This means that as operations became complex, the processor was needed to decide how to execute user instructions, in order, out of order, multiple instructions at the same time. This gave birth to SIMD and SIMT superscalar processors.
SIMD and SIMT
A SIMD processor is a processor technique where similar data sets are queued in the pipeline and executed in parallel. This is especially useful in graphic manipulation. SIMD designs improve the multimedia experience.
SIMT, on the other hand, refers to Single-Instruction Multiple Thread and is where different data sets that require the same operation are queued in the pipeline and executed using multiple threads. I.e. there is no need to fetch the same instruction for different data sets each time. Do it only once.
Examples of SIMD processors include Intel x86, Pentium with MMX extensions, Intel with SSE extension, AMD with SSE extensions, ARM neon among others.
Still, parallel processing has not improved processor speed much. For example, the Pentium 4, which was expected to clock 10GHZ, is stuck at 2GHZ. Still, SIMD has one advantage; it is kickass when it comes to processing multimedia and graphics. SIMD processors gave birth to graphic processing units.
What is a GPU?

A GPU is also called a graphics card, also known as a video card. But a GPU refers to the graphics processing unit which is the processor on the graphics card’s board. GPUs take information and turn it into frames. The speed of a GPU is measured in MHz and performance is measured by frame rate -how many frames it outputs per second.
GPUs put SIMT and SIMD techniques to practical use. They have various threads. So, every time they need to execute a particular instruction, all the data sets that need this instruction are pre-fetched and pipelined to be executed at the same time using the threads.
By focusing all of the computer's resources on a specific task, GPUs are advantageous as follows:
Better and powerful display

GPUs have a far better display than what you’d get from a CPU with an integrated graphics card. GPUs are dedicated types of processors designed primarily for quick image processing.
Useful in graphically intense applications

GPUs make graphically intense applications possible. They help in rendering images, videos, and animations to the screen. They make zooming, fast motion, and 3D rendering possible. GPUs also support complex mathematical operations needed to generate smooth motion and pictures. Virtual and augmented reality has also been made possible with GPUs.
50-100 times faster than CPUs in parallel processing tasks
Modern GPUs deliver immense processing power and memory bandwidth beyond what CPU counterparts are capable of. In tasks that require parallel architecture and multi-threading GPUs are 50 to 100 times faster than CPUs. They are used in the field of AI, data analysis, and machine learning.
For gaming PCs, you need more powerful graphics than your basic office PC. Frame-rate matters a lot when it comes to gaming but not for a workstation GPU.
Leading GPU manufacturers

One largest manufacturers of GPUs is Nvidia which provides a series of enterprise GPUs that go by Tesla, named after the 90’s era scientist of the same name. Nvidia aims to improve enterprise-level GPUs capability in advanced parallel computation while preserving durability.
The Tesla V100, for example, is said to be the most cutting-edge data center GPU in the world. It can achieve a 15.7 TFLOPS single-precision performance. Other GPUs from Nvidia include the GeForce 20 series which succeeded the GeForce 10 series and introduced ray-tracing tech allowing the blending of machine graphics with real-life scenes.
Nvidia offers gaming GPUs too, and these cost a bit cheaper than its enterprise offers because Nvidia is not the original enterprise manufacturer.
AMD is another top GPU manufacturer. Their AMD Radeon VII, for example, boasts of Mac OS support, something which Nvidia is yet to do.
But in terms of performance, no product in the AMD’s line beats Nvidia’s RTX 2080 Ti with real-time tracing, ai-guided super-sampling, and its RT and high-end cores. In terms of pricing, both brands have graphic cards for low, mid, and high-end markets.
Other GPU manufacturers worth mentioning include Intel with their integrated and XE graphics cards coming soon.
Disadvantages of GPUs
GPUs are not cheap; they’ll often take the most substantial part of your gaming budget. Remember GPUs are designed with more transistors, large high-end memory, and come attached with an expensive cooling solutions.
But you can get GPUs for lower prices, under 100 dollars, however, just know that this won’t be as efficient as the high-end design. For example, the cheap RX 550 that goes for $80-$90 can only run games at 1080p and lower settings.
What is an APU?
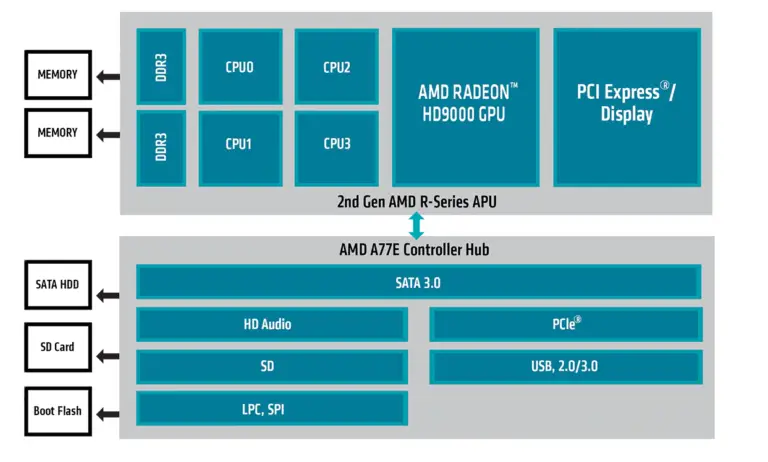
An Accelerated Processing Unit is a type of processor offered by AMD that can serve as a CPU and GPU at the same time. Most modern CPUs come integrated with GPUs, i.e., Integrated Graphics, but only the APU from AMD offers the combination of a GPU and CPU in a single die and HSA support.
AMD’s APU is a general-purpose processor. It has found application in the Microsoft Xbox and Sony PlayStation 4.
The best AMD APU series is the Ryzen series, which features an entirely new processing design. If you are looking to enjoy AMD’s latest advancements in CPU and GPU technologies on a single chip, check out Ryzen 5 3400G, Ryzen 5 2400G, and Ryzen 3 3200G.
Can I crossfire an APU with a GPU?

Yes, you can totally run an APU and a GPU in crossfire configuration as long as the APU card has CrossFire support. AMD CrossFire support is a technology that allows the use of multiple GPU cards on a single computer to boost graphics performance.
It all depends on the motherboard you are using to build your PC and the series of APU and GPU you intend to CrossFire. If after using the APU there is a GPU slot left, there is no reason at all; you shouldn’t get a GPU and run a crossfire configuration.
Most people will dismiss cross-configuration as a marketing gimmick and will tell you to invest in better RAM, better APU, or a stronger dedicated GPU, but there is an advantage. APUs lack onboard Video RAM and instead use the systems, but in crossfire configuration, the GPU VRAM is used, meaning less stress on the system and lower temperatures.
So, feel free to use a crossfire configuration. For example, an AMD a8-6600k and a Radeon HD 7770 at the same time is very much possible.
Conclusion
See. All that jargon, CPUs, GPUs, APUs is not difficult at all. A GPU is just a dedicated graphics card, a CPU can feature integrated graphics (IGPU), and an APU offers the best of both worlds on a single chip. For high-mathematical computations and graphics, dedicated graphics cards (GPUs) are the way to go.